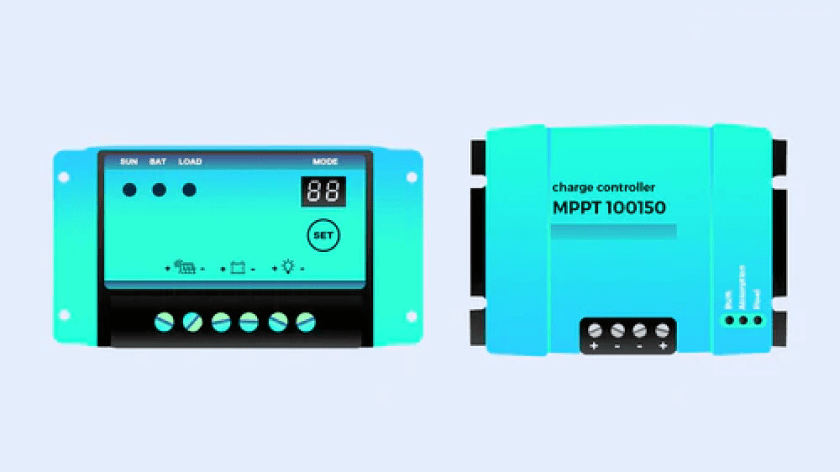
Two Major Types of Solar Charge Controller
We mentioned earlier what a solar charge controller works for: balance the voltage from solar panels array. Now let's talk about the types of solar charge controllers and how they differ.
The two major types of solar charge controllers are: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controllers & Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers.
PWM controllers
PWM regulation strategically meters solar voltage to batteries at fixed conversion rates. Ideal for smaller, simpler setups, these controllers offer low-cost, low-maintenance operation well-suited to entry-level systems.

However, their functionality is limited to fixed solar panel configurations, and they tend to be less efficient than their MPPT counterparts. It reduces their current output gradually as the battery charges. Once the battery reaches 100% charge, the controller can keep it full by providing small amounts of power without overcharging.
PWM solar charge controllers are designed to be used with solar panels that match the battery voltage. For example, if you want to charge a 12V battery, you also need photovoltaic modules with a rated output of 12 volts.
Pros:
- More affordable than MPPT charge controllers
- Smaller and easier to carry around
- Suitable for DIY solar energy systems
Cons:
- You cannot charge batteries with higher-voltage solar panels
- Less efficient than MPPT charge controllers
- Less efficient in cold weather
MPPT controllers
MPPT controllers are more efficient and versatile, better suited for larger and more complex solar systems. They can track the maximum power point of the solar panel, providing up to 30% more power than a PWM controller, and can work with any type of solar panel configuration.

However, their increased performance comes at a higher price point compared to PWM controllers. Despite the price, solar charge products with MPPT controllers are more popular on the market.
An MPPT charge controller can match a battery system with solar panels of higher voltage, keeping your solar panels at the ideal voltage and current for maximum power output. At the same time, the controller keeps a suitable charging voltage for the battery system.
As a quick example, assume a small solar array is operating at 36 volts and 10 amps, providing 360 watts of power. Using a PWM charge controller, you cannot use this power output to charge a 12V battery. However, an MPPT charge controller can lower the voltage to 12 Volts while increasing the current to 30 amps, which makes charging possible.
Pros:
- You can charge batteries with solar panels of higher voltage
- Up to 20% more efficient than PWM charge controllers
- Can handle higher wattages efficiently
Cons:
- MPPT technology is more expensive
- Installation is more complex
- Less efficient in systems smaller than 170W
Tips for Choosing PWM & MPPT
Whether selecting a PWM or MPPT charge controller, carefully match specifications to your particular solar panel and battery system. This ensures optimal and efficient performance for many years.
While MPPT controllers deliver the highest energy yields of up to 95%, PWM options remain a cost-effective choice for simpler applications. Consider if their slightly lower 70-80% efficiency still meets your needs.
Always confirm voltage and current ratings align between all components to avoid damage. An undersized controller leaves energy on the table, while an oversized one risks component harm.
Factor in efficiency gains from MPPT controllers that maximize solar harvesting versus PWM alternatives. The added cost may prove worthwhile for off-grid or battery-hungry loads.
Monitoring and temperature compensation features allow fine-tuning your system and extending battery life. An LCD display provides at-a-glance status checks too.
Research warranties, features, and reputable brands to find a quality controller tailored to your budget and application needs. With the right selection, your solar investment will power dependably.



























































Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.